When Apple fans wait in long lines for a new iPhone or Harley-Davidson riders proudly get tattoos of the brand logo, something deeper than product features is happening. These brands have mastered emotional branding, a strategy that builds powerful customer connections that go far beyond a normal buyer–seller relationship.
Emotional branding is not just about highlighting product benefits or offering competitive pricing. It taps into consumer emotions, brand perception, and psychological triggers to create genuine, long-term loyalty. Brands that connect emotionally become more memorable, more trusted, and harder for competitors to replace.
This guide will help you understand how emotional marketing works and why it plays such an important role in brand loyalty, customer experience, and long-term relationship building. You’ll learn simple but effective techniques to strengthen your brand identity, create authentic storytelling, and build emotional connections that turn regular buyers into passionate brand advocates.
The Psychology of Emotional Branding: How Emotions Influence Customer Buying Decisions
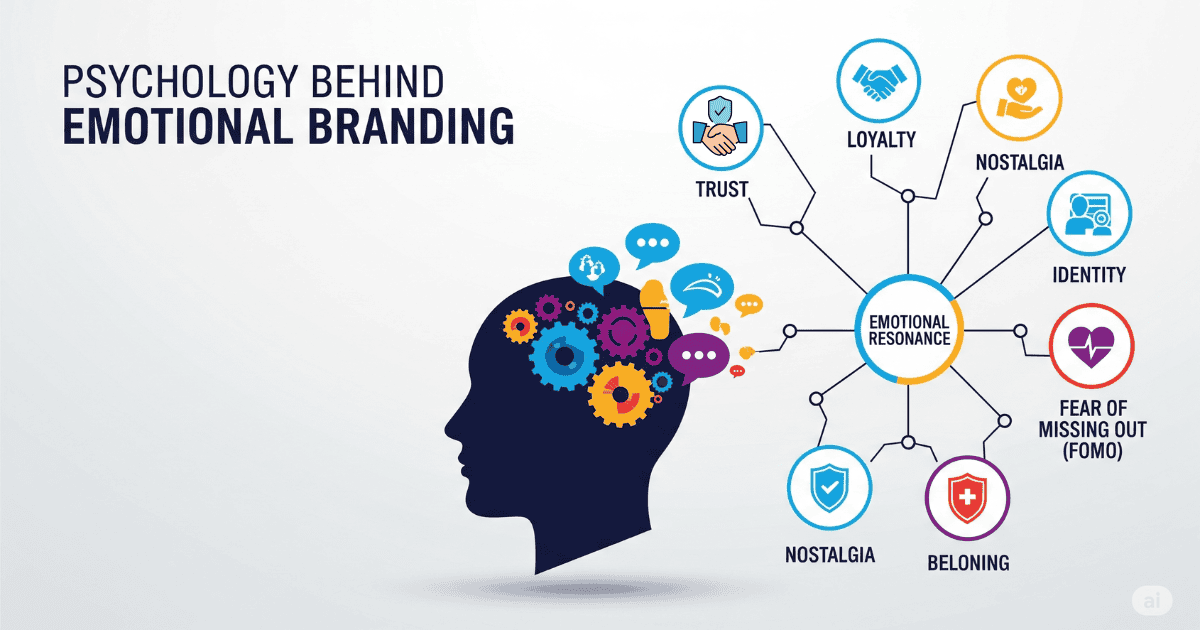
Consumer psychology shows that emotions drive most buying decisions. Studies in neuroscience even reveal that people who lose the ability to process emotions struggle to make basic choices. This proves how strongly feelings influence what we buy and which brands we prefer.
Emotional branding uses this truth to build deep, personal connections with customers. When people feel emotionally attached to a brand, they become less sensitive to price and more loyal—even when mistakes happen. These emotional bonds also encourage word-of-mouth marketing, which is one of the most powerful and authentic forms of promotion.
Great emotional marketing strategies understand that people don’t just buy products. They buy identity, meaning, and aspiration. A luxury watch represents status and success. A sports drink represents performance and motivation. A skincare product represents confidence and self-care.
When brands understand these deeper motivations, they can position themselves as partners in a customer’s journey—not just sellers of a product. This is what creates strong emotional connections, deeper brand loyalty, and long-term customer relationships.
The Foundation of Emotional Branding: Building Brand Trust and Authenticity
Creating strong emotional connections starts with trust and authenticity. Customers can easily spot insincerity, and nothing harms emotional branding faster than manipulation, overpromising, or fake messaging.
Authentic brands show consistency between what they say and what they actually do. Patagonia is a great example. Their commitment to environmental responsibility is genuine. When they launched the “Don’t Buy This Jacket” campaign, they encouraged customers to think carefully before buying new clothes. This reinforced their values, even though it could reduce short-term sales.
Transparency is another key driver of brand trust. Brands that openly share challenges, admit mistakes, and show vulnerability feel more human and relatable. This level of honesty strengthens emotional connections and improves brand credibility.
Consistency across every touchpoint—ads, website content, customer service, packaging, and product quality—also matters. When customers experience the same brand values and personality everywhere, their trust grows. Over time, this consistency helps build deep emotional loyalty that competitors can’t easily break.
Crafting Compelling Brand Storytelling for Stronger Emotional Connections

Brand storytelling turns a business from a faceless company into something with personality, purpose, and emotion. Stories resonate deeply because people naturally connect with narratives that reflect their own dreams, challenges, and experiences.
Great brand stories usually follow a simple structure:
- a relatable hero (often the customer)
- a problem or challenge
- a journey of growth
- and a transformation where the brand plays a helpful role
This structure works because it lets customers see themselves in the story. The brand becomes the guide—not the hero—helping customers succeed or improve their lives.
Nike is a perfect example. Their “Just Do It” campaigns rarely talk about shoe features or product specs. Instead, they highlight real people overcoming obstacles, pushing limits, and achieving greatness. These universal themes—perseverance, discipline, achievement—connect emotionally with athletes of all levels.
Small businesses can also use storytelling effectively. A local café can share stories about the farmers behind their coffee beans, the community events they support, or the daily moments they create for customers. These authentic narratives build emotional loyalty that competitors can’t easily replace.
The best brand stories are the ones customers want to share. When people feel emotionally connected to your brand narrative, they naturally recommend your business, talk about their experiences, and help spread your message without being asked.
Leveraging Emotional Triggers in Marketing
Emotional triggers are specific psychological motivators that drive immediate responses and long-term loyalty. Understanding and ethically leveraging these triggers allows brands to create more impactful customer experience marketing.
Fear of missing out (FOMO) is a powerful trigger that creates urgency and desire. Limited-time offers, exclusive access, and scarcity messaging tap into this emotion. However, successful emotional branding uses FOMO authentically rather than manipulatively, creating genuine value for customers who act quickly.
The desire for belonging drives many purchase decisions, particularly for lifestyle and identity-related products. Brands like CrossFit have built entire communities around shared values and experiences, making customers feel part of something larger than themselves.
Nostalgia evokes positive emotions associated with past experiences, making it particularly effective for brands with heritage or those targeting specific generational memories. Coca-Cola frequently uses nostalgic imagery and messaging to reinforce its position as part of cherished family moments and cultural traditions.
Achievement and recognition appeals tap into customers’ desires for success and acknowledgment. Loyalty programs, milestone celebrations, and personalized achievements create emotional satisfaction that extends beyond the immediate purchase.
Building Long-Term Customer Relationships
Creating lasting customer emotional connections requires consistent effort and genuine care for customer well-being. Transactional relationships focus on individual sales, while emotional relationships prioritize lifetime value and mutual benefit.
Personalization plays a crucial role in relationship building. Modern customers expect brands to understand their preferences, anticipate their needs, and provide relevant experiences. However, effective personalization goes beyond using someone’s name in emails—it involves understanding their motivations, challenges, and goals.
Regular, meaningful communication helps maintain emotional connections over time. This might include educational content that helps customers achieve their goals, updates about brand initiatives they care about, or simple check-ins that show genuine interest in their well-being.
Customer service interactions often determine the strength of emotional bonds. When problems arise, how a brand responds can either strengthen or destroy emotional connections. Companies that empower service representatives to go above and beyond create memorable experiences that deepen customer loyalty.
Successful brands also create opportunities for customers to connect with each other, building communities around shared interests and values. These peer-to-peer connections strengthen overall brand attachment and create network effects that drive retention and acquisition.
For Further Reading: Sustainable Branding Strategies That Build Trust and Drive Growth
Measuring Emotional Brand Connection
While emotions might seem difficult to quantify, several metrics can help brands assess the strength of their customer emotional connections and the effectiveness of their emotional branding efforts.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) measures customer willingness to recommend a brand, which often reflects emotional attachment rather than mere satisfaction. Customers who feel emotionally connected are more likely to become brand advocates.
Customer lifetime value (CLV) indicates the long-term impact of emotional connections. Emotionally attached customers typically make more frequent purchases, choose higher-value options, and remain loyal longer, resulting in higher CLV.
Social media engagement metrics reveal emotional investment levels. Customers who feel emotionally connected are more likely to like, share, comment, and create user-generated content about brands they love.
Brand sentiment analysis through social listening tools provides insights into how customers feel about brands and what emotions drive their relationships. This qualitative data complements quantitative metrics to provide a complete picture of emotional brand performance.
Customer retention rates and churn analysis help identify when emotional connections weaken and what factors contribute to relationship deterioration.
Common Emotional Branding Mistakes to Avoid

Several common pitfalls can undermine emotional branding efforts and damage customer relationships. Understanding these mistakes helps brands develop more effective strategies.
Forced authenticity often backfires when brands try too hard to appear relatable or trendy. Customers quickly detect insincerity, and perceived manipulation damages trust more than remaining professional and straightforward.
Overemotional messaging can feel overwhelming or manipulative, particularly when not balanced with rational benefits. Effective emotional branding combines feelings with practical value.
Inconsistent brand personality across channels confuses customers and weakens emotional connections. Brands must ensure their emotional identity remains consistent whether customers interact through advertising, websites, social media, or customer service.
Neglecting negative emotions can limit brand effectiveness. While positive emotions drive attraction and loyalty, addressing negative emotions like frustration, anxiety, or disappointment can create equally strong connections when handled with empathy and solutions.
Short-term thinking undermines long-term relationship building. Emotional branding requires patience and consistent investment, as authentic connections develop gradually through repeated positive interactions.
The Future of Emotional Customer Connections
Technology continues to create new opportunities for emotional branding while also raising important considerations about privacy and authenticity. Artificial intelligence and machine learning enable more sophisticated personalization and emotional recognition, but brands must balance technological capabilities with human connection.
Virtual and augmented reality technologies offer immersive experiences that can create powerful emotional memories. Brands experimenting with these technologies must ensure the emotional impact aligns with their overall brand identity and values.
Social commerce and community-building platforms provide new venues for fostering emotional connections through shared experiences and peer interactions. Brands that successfully integrate commerce with community often achieve stronger emotional bonds.
Sustainability and social responsibility increasingly drive emotional connections, particularly among younger consumers. Brands must demonstrate genuine commitment to causes their customers care about, as superficial efforts often generate negative emotional responses.
Building Your Emotional Branding Strategy
Developing an effective emotional branding strategy starts with understanding your customers’ deeper motivations, values, and aspirations. This requires going beyond demographic data to explore psychological and emotional drivers.
Begin by identifying the primary emotions you want associated with your brand. These should align with your target audience’s needs and your company’s authentic capabilities. A financial services company might focus on security and confidence, while a fitness brand might emphasize empowerment and achievement.
Audit your current brand touchpoints to assess emotional consistency. Review your messaging, visual identity, customer service protocols, and product experiences to ensure they reinforce your chosen emotional positioning.
Develop content and experience strategies that consistently deliver your target emotions. This includes everything from advertising creative to packaging design to post-purchase follow-up communications.
Train your team to understand and support your emotional branding goals. Every employee interaction with customers should reinforce the emotional connections you’re building.
Emotional branding represents a fundamental shift from selling products to building relationships. When done authentically and consistently, it creates competitive advantages that persist long after specific products become outdated or market conditions change. The brands that master emotional connections don’t just win customers—they create communities of advocates who choose to be part of something meaningful. Start building these connections today, and watch as your customer relationships transform from transactions into lasting partnerships.
FAQs
1. What is emotional branding and why is it important?
Emotional branding is a strategy that focuses on creating meaningful emotional connections between a brand and its customers. It’s important because emotions influence most buying decisions, helping brands build long-term loyalty, increase customer retention, and stand out from competitors.
2. How do brands build emotional connections with customers?
Brands build emotional connections by staying authentic, telling compelling stories, solving customer problems with empathy, delivering consistent experiences, and aligning with customer values. Personalization and memorable customer service also play a major role.
3. What are examples of successful emotional branding?
Some of the best examples include Apple’s community-driven product launches, Nike’s motivational storytelling, and Coca-Cola’s nostalgic campaigns. These brands focus on identity, belonging, and emotion rather than just product features.
4. How can small businesses use emotional marketing effectively?
Small businesses can use emotional marketing by sharing real stories, showing the human side of their brand, supporting local causes, personalizing interactions, and creating community-focused experiences. Authenticity matters more than budget.
5. How do you measure emotional connection in marketing?
Brands measure emotional connection using metrics like Net Promoter Score (NPS), customer lifetime value (CLV), social media engagement, sentiment analysis, reviews, and customer retention rates. These indicators show how deeply customers connect with the brand emotionally.




